Are you using SEO effectively to boost your business?
SEO is essential to deliver traffic, authority, leads, and sales, but you’ll only get those benefits if you do it right.
If not, your business might as well be invisible online, and who wants that, right?
We know it’s not always easy to stay up to date, but you can’t relax when it comes to SEO.
Google’s always tweaking its search algorithms, so there’s no guarantee that SEO practices that worked in the past will keep working in the future.
That’s why you have to stay up to date with the latest SEO guidelines if you want your business to succeed.
We’re here to help.
Our in-depth guide contains the latest SEO best practices so you can improve how your content appears in search results, and get more traffic, leads, and sales.
There’s a LOT of info here, so we’ve put together a table of contents so you can jump straight to your preferred starting point.
- What Is SEO?
- How Does SEO Work?
- The Top SEO Ranking Factors
- Understanding Keywords and Keyword Intent
- Where To Use Keywords For SEO: 7 Key Locations
- How To Perform The Ultimate SEO Audit
- How To Build Links For SEO
- Social Media And SEO
- Mobile SEO Guide
- The Best Keyword Research Tools
- How To Use SEO For Lead Generation
- FAQs About SEO
Let’s start with a definition of what SEO is, just so we’re on the same page.
What Is SEO?
SEO means search engine optimization. It’s the practice of increasing the search engine rankings of your web pages so that they appear higher in search results, bringing more traffic to your website.
SEO can also stand for search engine optimizer. That’s a person who does search engine optimization.
Search engine optimization efforts aim to increase organic traffic. That’s the traffic you get when visitors click a link in search results to get to your site. That’s in contrast to paid traffic, which comes from ads.
Most SEO focuses on optimizing for Google’s search engine, which dominates the overall search market with a share of over 90%. However, it is also possible to optimize for other search engines like Bing, Yahoo, Baidu, and others.
SEO activities are usually broken down into two main types: on-page SEO and off-page SEO.
What Is On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is all about optimizing content, code, and other parts of your website that you control.
Off-page SEO means taking action to build trust, authority, social signals, and inbound links.
You need both types of optimization in your SEO strategy.
Now that that’s clear, let’s look in more detail at how SEO works.
1. How Does SEO Work?
To understand how SEO works to improve search rankings, we’ll need to break it down a little.
What Is Search Ranking In SEO?
When you talk about search ranking in SEO, you’re talking about the position of your content on search results pages (SERPs).
If you have a #1 ranking, your web page appears first in SERPs. That puts it at the top of the page unless there’s a promoted result (which is an ad) or an answer box above it. We’ll talk more about answer boxes later in this guide.
Ideally, you want your web page content to appear as one of the top three results. That’s because those positions get almost half of the clicks in SERPs, and more clicks mean more traffic and more potential for leads and sales.
Even if your web page isn’t in the top three, it’s still great if it shows up on the first page of SERPs. If it doesn’t, you’ll definitely miss out on organic traffic, as 95% of people only look at the first page of SERPs.
How Does Google Search Work?
To understand SEO, you’ll also need to know how Google search works.
Google aims to deliver relevant search results as part of its bid to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful”.
To do that, the search engine has to know what information is out there. Here’s how that process works.
- Google has automated software called search bots or spiders. These bots visit web pages in a process called crawling the web.
- Then they add the pages they crawl to Google’s index, which is a huge catalog of trillions of web pages.
- When people search, Google shows the most relevant results from that catalog.
People usually type or say words related to what they are looking for. These are called keywords, and as you’ll see, they are an important part of SEO. We’ll look at those in more detail later in this guide.
Understanding Google’s Search Quality Ratings
Another important part of the search process is the quality of your content. Google has search quality ratings which assess this.
The ratings look at:
- How expert, authoritative, and trustworthy the content is
- Content quantity and quality
- Site information, including who’s responsible for the site
- Website reputation
These guidelines help Google decide which results are most relevant, useful and trustworthy. The most relevant results appear first in SERPs, with less relevant results shown later.
When you do SEO, you’re helping Google’s spiders to crawl and understand your content. You’re also telling Google your content is relevant to certain queries, so your web pages show up in the right search results.
How To Check Your Search Engine Rankings
One of the first steps in improving SEO is to know where you’re starting from. That means checking your search engine rankings.
Here are a couple of ways to do that.
The easiest way is just by searching the terms you want to rank for. To do that, first, open a private or incognito browser window and search Google. Use the terms you think your customers will use to find your site, then check the results.
But what if you have a large, established website, or want to find other terms you might be ranking for?
In that case, you’ll have to use a tool. One of our favorite online toolkits is SEMrush, which includes a variety of tools for SEO, content marketing, and search engine marketing.
Here’s how you find search engine rankings for your web pages with SEMrush.
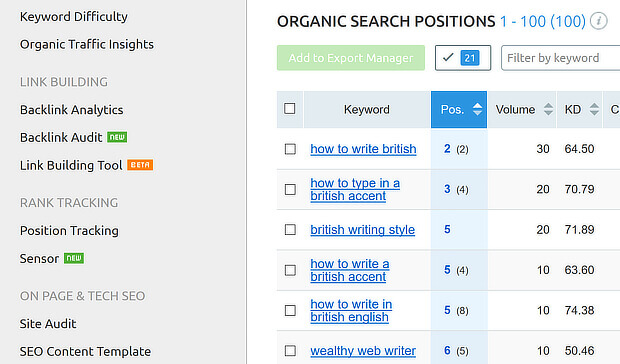
Go to SEO Toolkit » Organic Research » Positions and type in your domain name. Scroll down to Organic Search Positions to see which keywords your content ranks for and what ranking position it holds.
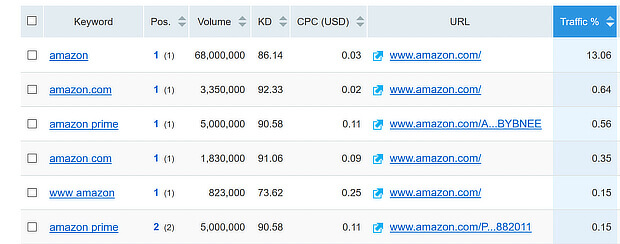
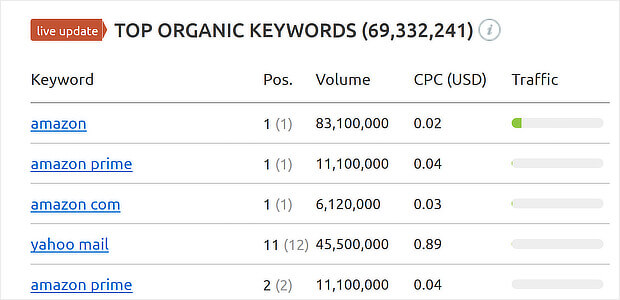
Or you could navigate to Domain Analytics, type in your domain name, and see all the keywords you currently rank for, as in this search for Amazon:
Now, let’s look at what Google uses to determine which web pages have a good search engine ranking. These are called SEO ranking factors.
2. The Top SEO Ranking Factors
If you’re looking for the top search engine ranking factors, the answer isn’t a million miles away. Google’s been clear on its top three:
- Links
- Content
- RankBrain, or user experience
Let’s look at these in more detail.
1. Links
Links are a crucial SEO ranking signal because they’re what the web is built on. When you’re talking search engine ranking, three types of links matter:
- Inbound links – links coming to your site from external web pages
- Outbound links – links from your web pages to external sources
- Internal links – links within your site to your own content
Inbound links help Google figure out if your content is relevant and authoritative. As we mentioned, if your web page gets a link from a site that’s already an authority, that link is more valued than a link from a low-quality site.
In contrast, low-quality inbound links can hurt your search ranking, so keep those to a minimum. We’ll explain how to do that in a minute.
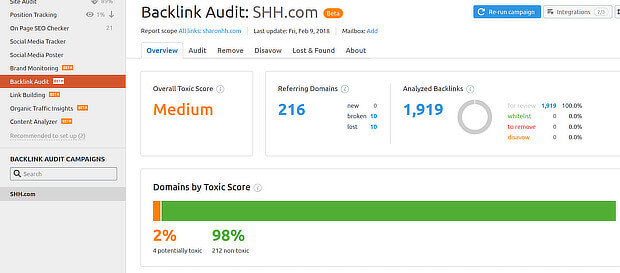
To find your inbound links with SEMrush, you’ll need to set up a project to track key metrics for your domain. Then go to SEO Toolkit » Link Building » Backlink Audit. This will bring up an overview report. At this point there are two things you can do:
First, to find low-quality backlinks, look at the Domains by Toxic Score section.
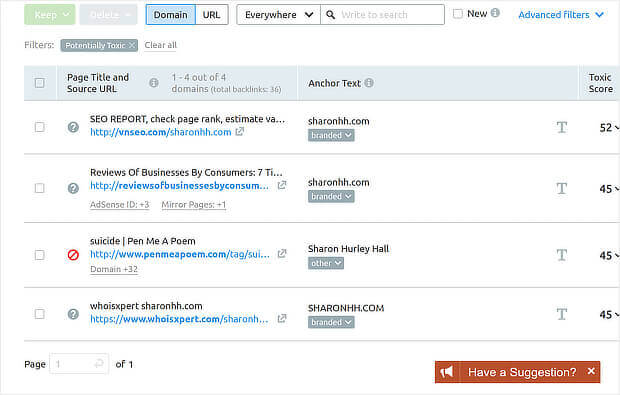
Click on the toxic percentage to see suspect inbound links.
Then you can choose to keep or whitelist those links (if they’re not really toxic) or remove or disavow them if they are. Google suggests website owners exercise caution with link disavowal.
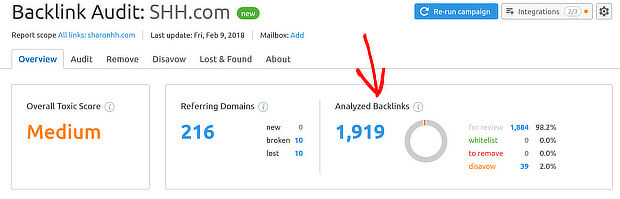
Here’s the second way to check out your inbound link profile:
Go back to the main Backlink Audit report in SEMrush, and click on Analyzed Backlinks to see inbound links.
In terms of outbound links, it’s important to create links to authoritative sites relevant to your topic. This shows visitors and Google that you’re creating quality content. Often, you will find authoritative content when researching a content topic. Then you just need to make a note of it so you can add it to your content.
You can also increase the value of your own pages by interlinking your content to create internal links. An authoritative page can pass on search ranking or link juice to other pages on your site. So if you have an in-depth resource, you can link to it every time you talk about your topic.
You can learn more about the importance of links for SEO in our ranking factors guide.
2. Content
Content is the second major SEO ranking factor and is just as important as links. As we’ve said, relevance and quality are two crucial factors for search engine rankings.
There are several areas to optimize here. Aside from keywords, which we’ll look at in a later chapter, it’s essential to understand what people mean when they type in a search term. This is called search intent.
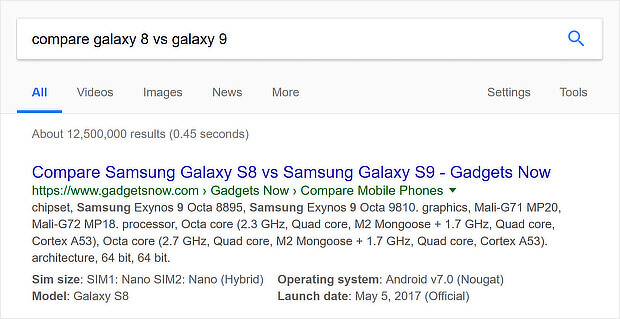
Sometimes the intent is clear, like when they type in “compare” or “buy.
But at other times, you’ll have to think more carefully. For example, if you want to rank for “arizona real estate”, you might think it’s a good idea to optimize your content for people wanting to move to a house in Arizona. But it might turn out that the people searching for that term are realtors looking for a property they can list.
Optimize for the wrong search intent, and your page will never rank.
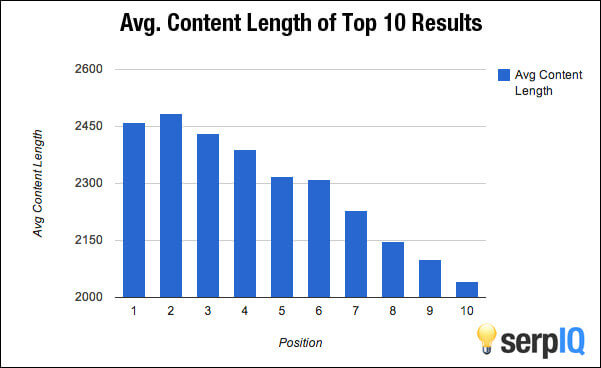
There’s one more thing. The research shows that the length of your content can also be important. That’s because content that’s more than 2000 words long tends to get more top ten places in SERPs.
Longer content also gets more links (another ranking factor) and more shares. As we’ll see, shares can contribute to an indirect ranking factor: social signals.
So, it doesn’t hurt to include longform content in your content strategy when you’re thinking about SEO.
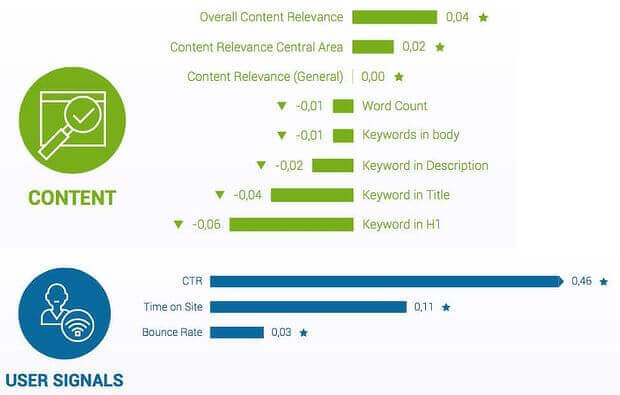
3. RankBrain (User Experience)
The third major SEO ranking signal is Google’s artificial intelligence search ranking algorithm. The company calls it RankBrain, and it’s all about user experience.
There are three important aspects of RankBrain:
- Clickthrough rate: the percentage of people visit your site from a SERPs entry
- Bounce rate: how many people bounce a short time after following a SERPs entry to your site. A quick bounce means they didn’t get what they wanted
- Dwell time: how long they stick around on your site after arriving. Clearly, longer is better, as it means your site delivered what they wanted
Together, these tell Google how users interact with your site and if your content is relevant, which can affect search ranking. Learn more about RankBrain and SEO here.
Other SEO ranking factors include accessible URLs, domain age (older is usually better), page speed, mobile-friendliness, business information, and technical SEO. We’ll look at some of those ranking factors in more detail as we go through the guide.
And check out this article for even more information on SEO ranking factors.
3. Understanding Keywords and Keyword Intent
Before we go any further, let’s recap some key terms:
- Keywords are words and phrases that describe what your content is about and what people are searching for
- Keyword research is about finding those terms so you can use them properly in content optimization and SEO in general.
Why Do Keyword Research?
Keyword research can:
- Help you identify topics your target audience is looking for
- Understand what people really want when they enter particular search terms
- Show you the terms competitors are targeting so you can beat the competition
- Help you streamline and target all marketing activities
We’ll talk more about how to use the keywords you find in a later section, but for now, we’ll focus on the research process itself.
Before we do, let’s look at some different ways of thinking about keywords.
As we’ve said, it’s useful to think about what searchers intend to find when they enter a particular word or phrase. That’s called keyword intent, which is like the search intent mentioned earlier.
Understanding Keyword Intent
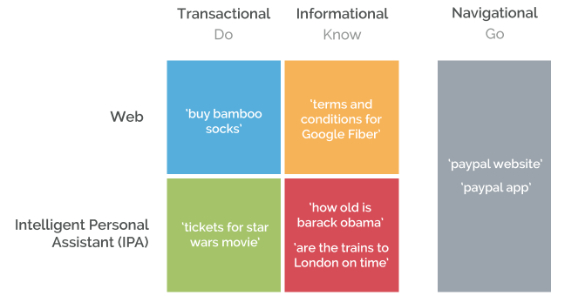
There are four ways to categorize search intent:
- Navigational: when trying to find a particular site
- Informational: when searching for the answer to a question
- Investigational: pre-purchase searches
- Transactional: when searchers actually want to buy
Ideally, you’ll optimize your content for all those types of searches. Learn more about content optimization for SEO here.
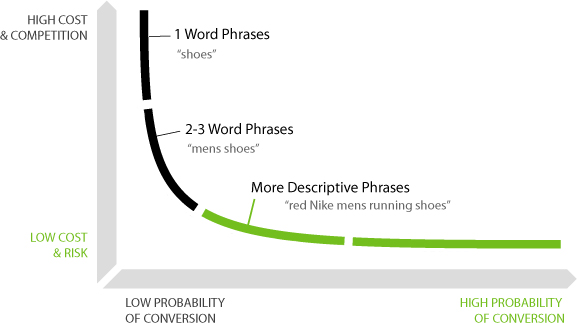
Types Of Keywords
Here’s another way to think about keywords. You can describe them as head, body and longtail keywords:
- Head keywords are generally no more than 1 or 2 words, with a high search volume.
- Body keywords are usually 2 to 3-word phrases with a medium search volume.
- Longtail keywords are phrases of four or more words with a low search volume. Most web traffic comes from longtail keywords.
Other ways to describe these keyword types include head, modifier, and tail keywords or short, medium and longtail keywords.
Google also has its own way of segmenting search queries, as Moz explains:
Their search evaluation quality guidelines list four types of searches:
- Know (finding information) or Know Simple (finding specific answers)
- Do (performing an action), including Device Action (like installing a mobile app after a search)
- Website (finding and visiting a site)
- Visit-in-Person (taking physical action based on search results, like going to a restaurant)
LSI Keywords
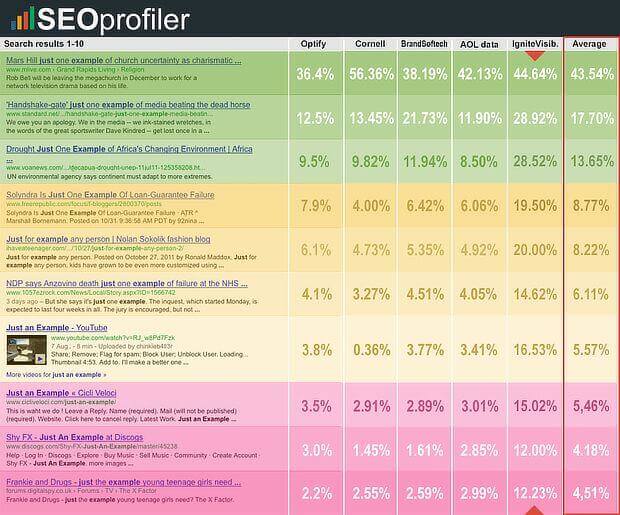
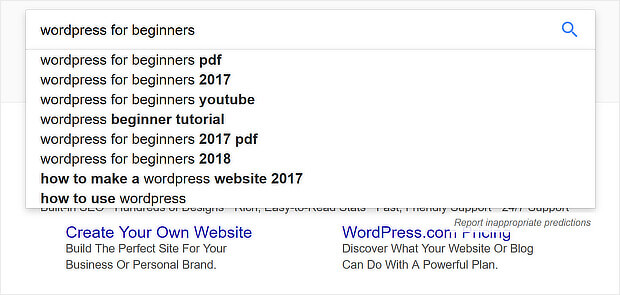
Two more terms people use for keywords are LSI keywords or semantic keywords. LSI stands for latent semantic indexing, which is a kind of smart word association search engines use to figure out what to show searchers. This can help search engines decide whether to show results for the movie or the ship when a searcher looks for information on “Titanic”.
As you’ll see below, you can see LSI keywords in action in any autocomplete search.
We’ll explain more about how to find LSI keywords in the next section. And you can see the section on where to use keywords for more information on integrating these keywords into your SEO content strategy.
Whichever way you choose to categorize keywords, one of the most important steps in SEO is doing keyword research. We’ll look at that next.
How To Get Started With Keyword Research
A great starting point for doing keyword research simply involves your brain. Always begin by brainstorming and thinking about the kind of information your visitors will need from you.
Keep track of the keywords you think of in a list or spreadsheet, and keep this handy as you go through the keyword research process.
There are lots of ways to find keywords for SEO. One of the simplest is to use the autocomplete function in Google. Start to type, and the suggested phrases are keywords you could consider.
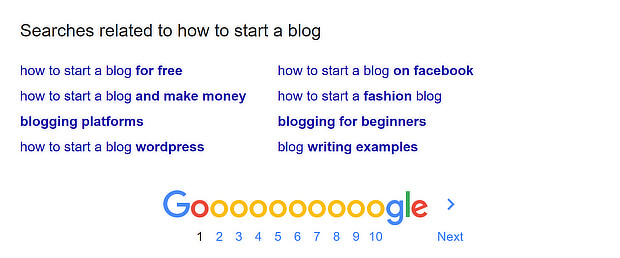
You can also complete a search and look at the terms that appear in the “searches related to” box at the bottom of SERPs.
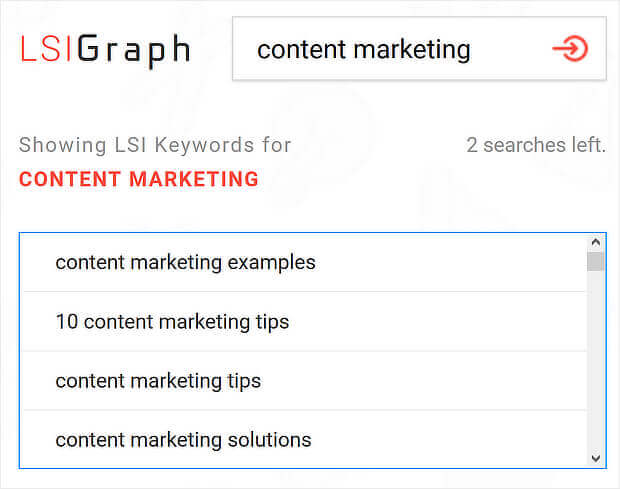
Both those methods will give you some of the LSI or semantic keywords we mentioned earlier. But if you want to find even more of them, you can use LSIGraph to discover longtail terms related to your main keywords. Just type in your keywords, and you’ll usually get a pretty long list.
You can also use dedicated keyword research tools to find keywords to use for SEO. Three of our favorite tools for this are:
Here’s a brief introduction to each tool.
How To Do Keyword Research With SEMrush
SEMrush makes some functionality available without logging in, but to get the best from it, you should create an account.
When you’re logged in, go to SEO Toolkit » Keyword Research » Keyword Overview. Type in your keyword phrase then click the Search button.
You’ll get in-depth data on search volume and trends, and on the top pages ranking for those keywords.
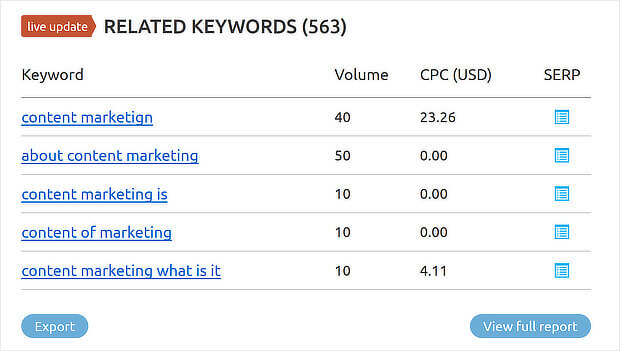
Scroll down to see the Related Keywords report, which will give you ideas for new keywords you can use for content optimization.
You can click on any keyword in the table to get a full report for that keyword.
Add suitable keywords to your list of target keywords, or click the Export button to export them into a spreadsheet.
Once you’ve found your keywords, use another SEMrush tool, the SEO Content Template, which is part of their Content Marketing Toolkit, to work out the best way to optimize your content.
Type in your keywords. SEMrush will analyze the top 10 results and suggest terms to include in your content to improve your ranking.
Want an alternative to SEMrush? You can also use Google Analytics to find SEO keywords for content optimization.
Learn more about using SEMrush for keyword research.
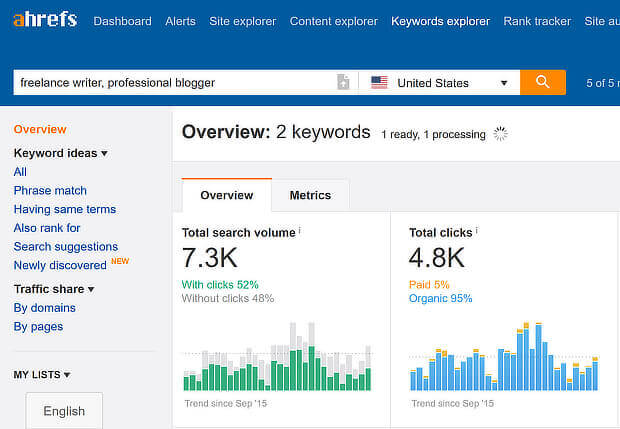
How To Do Keyword Research With Ahrefs
Like SEMrush, Ahrefs includes a lot of tools and has data on trillions of web links.
With Ahrefs, a good starting point for keyword research for SEO is the Keywords Explorer tool. Type in your terms, choose your country and search, and you’ll get an assessment of important related keywords and how difficult it will be to rank for those terms, known as “keyword difficulty”.
Ahrefs also includes a keyword ideas section that helps you identify related content terms, as well as the parent topic for your search term.
To get the most of this rich tool, make a note of new keywords you want to create content for, and keywords that can help you to optimize existing content.
Learn more about doing SEO keyword research with Ahrefs.
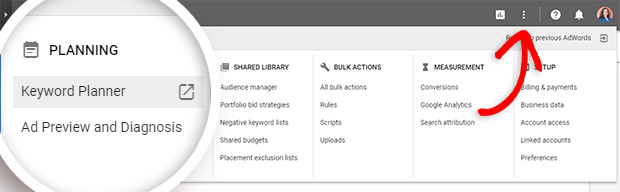
How To Use Google AdWords Keyword Planner
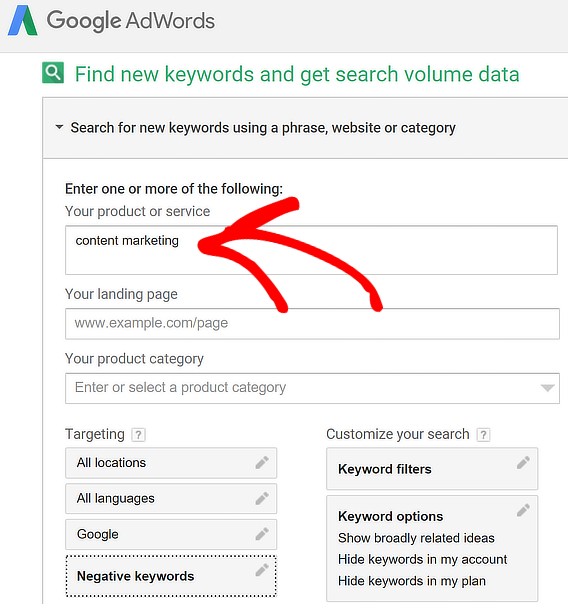
The Google Adwords Keyword Planner is meant to help with pay per click (PPC) advertising, but it also turns out to be a pretty decent keyword research tool for other content, too.
To use this, log in to your AdWords account and click on the three-dot menu. Choose Planning » Keyword Planner.
Next, go to Find new keywords and search volume data. Enter a couple of keyword phrases in the Product field.
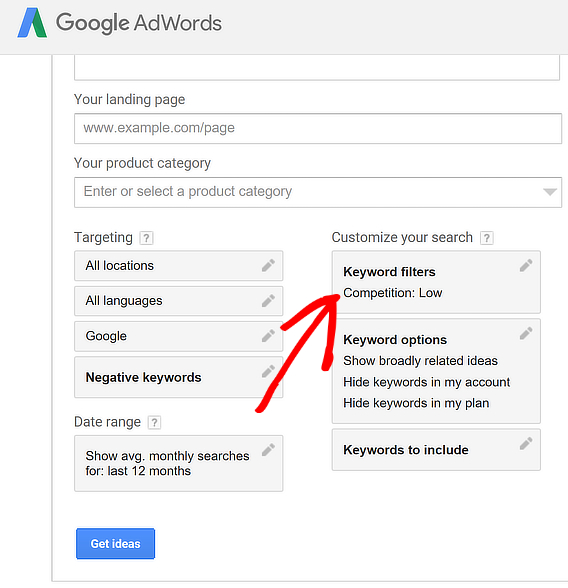
Use the on-screen filters to tweak your search.
For example, we’re going to look for keywords that have low competition, so we have a better chance of ranking. Save, then click Get Ideas.
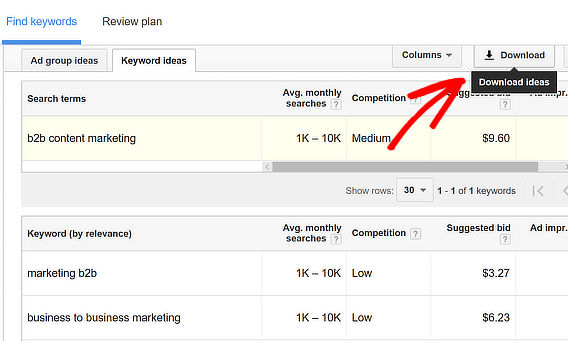
You’ll see the results in a table, which you can export to look at later.
It’s also worth looking Ad group ideas, which is another tab on the results page. This gives you some broad topics to consider for content.
Again, make a note of any you might want to add to your target keywords. Learn more about using the keyword planner for SEO.
How To Find Existing Keywords With Google Analytics
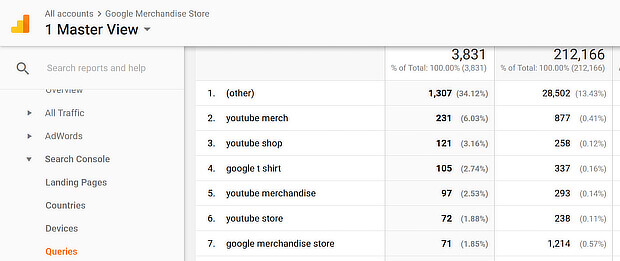
Another option for keyword research is to use Google Analytics to find the keywords people are already using to find your site.
To get the most data, link your Google Search Console account to your Analytics account. Then go to Acquisition » Search Console » Queries in your Analytics account. You’ll see a table with the keywords that bring traffic to your site.
Other ideas for finding keywords include:
- Seeing what people ask in social media updates or blog comments
- Social media hashtags
- Book categories on Amazon
And you can also include local search variants where relevant. We’ll talk more about local search later in this guide.
Learn more about keyword research here.
4. Where To Use Keywords For SEO: 7 Key Locations
Once you’ve found keywords, the next step is to create or optimize content around them.
The best practice is to focus each page of content on a single main keyword, though you should also use LSI keywords throughout your content.
Never use the same focus keyword more than once across your site, otherwise, you’ll compete with your own content for search rankings, and what would be the point of that?
A good starting point when using keywords for SEO is to identify existing pages that can use some optimization. SEMrush can help with this.
Navigate to SEO Toolkit » Organic Research » Positions. Then add your domain name. You’ll see which keywords your pages rank for already.
Take note of keywords where you have a ranking between 4 and 10. Those are good optimization candidates, as it likely won’t take much to help you achieve a top 3 ranking. If you recall, that’s where most of the clicks happen.
Once you have your keywords, there are several places to include them. Here are some of the most important ones.
1. Page Titles
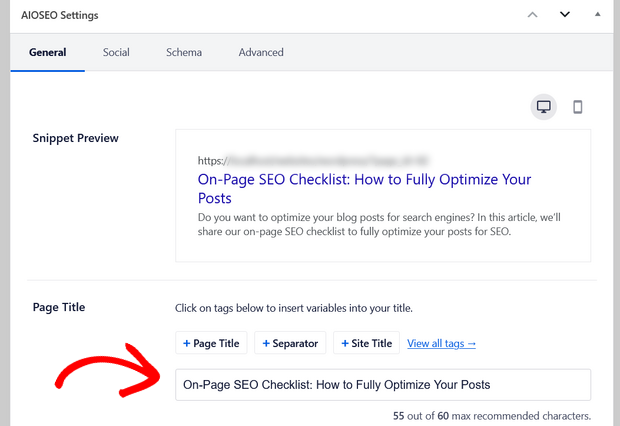
Page titles describe your page and are the first line of your search results entry. They tell both Google and searchers what your page is about.
Sometimes, the page title and the SEO title is the same; but you can also tweak the SEO title for better search ranking with a tool like All in One SEO.
For best results, place your target keywords at or near the start of your page title. That makes it look more relevant, and ensures it’s visible even on small screens.
Note that you never sacrifice readability to keyword placement: content is for people first. That’s so important that we’ll probably mention it again.
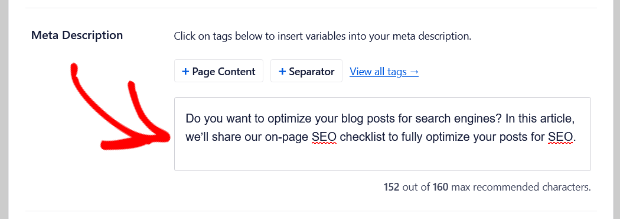
2. Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions show up under the title of a search results entry.
They describe the content and give another way to entice searchers to click. Meta descriptions aren’t a search ranking factor anymore, but they help Google work out if your content is relevant to a search term.
You can easily set your meta descriptions with All in One SEO as well. You can write them manually or use the smart meta tag generator with dynamic values like current year, month, author name, page content, custom fields, and much more.
3. Subheadings
The best web content is scannable because that’s how people read.
Subheadings will make them pause, and using keywords here will show readers that your content is relevant to what they were searching for. In other words, it tells your visitors they’ve come to the right place.
Keywords in subheadings also help Google understand what your content is about, and you can use LSI keywords here as well.
4. Content
As mentioned earlier, using keywords and LSI variations in content can help with search ranking. But it’s worth knowing that getting it wrong can hurt your search ranking.
What do we mean by wrong? One practice you must avoid is keyword stuffing, which is overusing the same keyword in a bid to artificially inflate rankings. Here’s how that could look:
We sell custom handmade suits. Our custom handmade suits are high quality. If you’re thinking of buying a custom handmade suit, please contact our custom handmade suit designers at [email protected].
We’ve got to tell you, Google HATES this.
So, how do you get it right? Here’s where you use keywords for best effect in content:
- In the first few sentences or first paragraph
- Throughout the content, varying the form as shown below
Write for people first, and you can’t go wrong with Google.
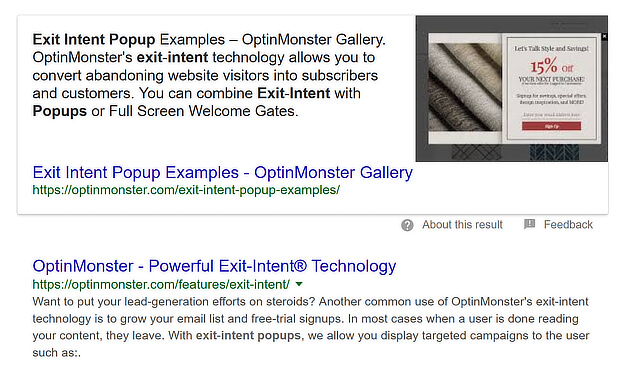
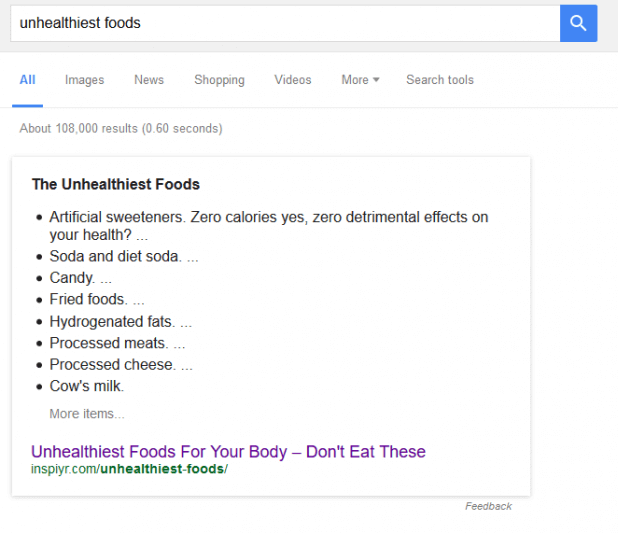
How To Optimize Content For Answer Boxes
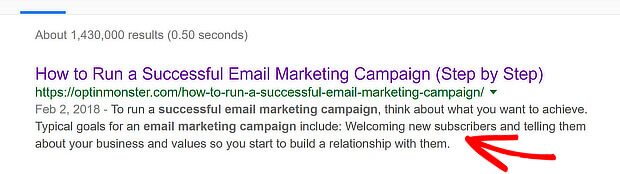
One thing you can’t ignore when optimizing content is answer boxes, which look like this:
That’s because these appear at the top of the search results to give immediate answers to searchers’ questions. Some people call this “position zero”.
This is a great place for your content to be, especially if your answer box makes people want to click through.
Google generates these automatically from content, but you can stack the odds in your favor by:
- Responding to questions
- Including questions as headings
- Creating relevant, factually correct answers of the right length (approximately 29 words according to Backlinko research)
- Including lists or tables in your answer
- Providing content for keywords that already have answer boxes
And of course, in all these cases, you’ll use some of the keywords from your research.
5. Images
Images are indexed, too, which means they’re a good place to use keywords. Ideally, you should optimize:
- Image file name, including a descriptive keyword where appropriate
- Alt text, which describes the image, and helps with accessibility
- Caption, if you use one
6. URLs
Your URL can help guide people and Google to what your page is about, so it’s a good place to include keywords. BUT avoid keyword stuffing your URL like the example below from Moz:
Instead, just make it descriptive, like this example from our site:
Check out our guide to using keywords for SEO and our on-page SEO checklist for more help with this.
7. Links
As we mentioned earlier, links are one of the top SEO ranking factors. The important thing to know about using keywords for SEO is that you should vary anchor text keywords for both internal and inbound links. Anchor text is the words that form a link, often underlined in blue.
For example, if you’re running a guest blogging campaign across multiple sites, don’t use identical anchor text for every bio. That’s a red flag for Google. Instead, vary the bio. Another version of the bio below could use the author’s name as anchor text instead of the word “website”:
You can also use keywords in social media, which we’ll look at in a later section, and for external directory and business listings.
Local SEO
If you’re targeting a particular locality, then it’s a good idea to tackle local SEO. This is also important when optimizing for mobile.
You can quickly discover how your site looks in local search by searching in an incognito window and seeing what comes up. Including real business information is an SEO ranking factor, so you’ll want to see:
- The name, address, and phone number of your business
- A business listing, such as Google My Business
- Your search ranking for your target local keywords
- Reviews of your business.
Two tools to help with local SEO are BrightLocal (for rankings) and MozLocal (for local search optimization).
Until now, we’ve been focusing on starting from scratch with SEO, but if you have an existing site, it’s also important to make sure it’s compliant with the latest SEO guidelines. To figure that out, you’ll need to do an SEO audit. We show you how in the next section.
5. How To Perform The Ultimate SEO Audit
One important aspect of taking care of SEO is identifying issues that are hurting search engine rankings and reducing the traffic you get from SERPs.
To ensure you’re getting the right results, you need to assess your existing traffic and carry out a website health check by doing an SEO audit.
In general, this means looking at on-page and off-page SEO, as well as technical SEO issues. Here are some of the key SEO audit steps you need to carry out.
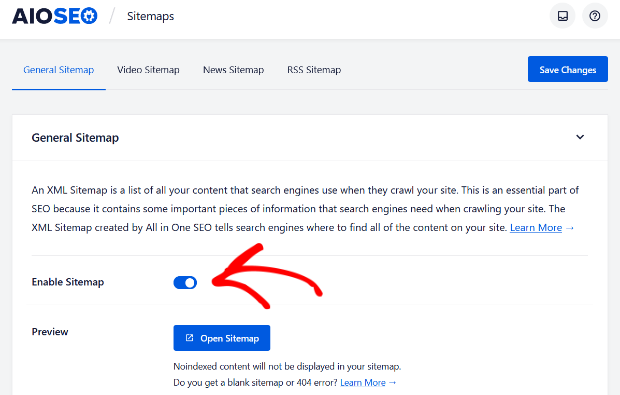
Step 1: Make Your Site Crawlable
An accessible URL is an important SEO ranking factor. Ensure that Google can crawl your site to find your content and know what it is about. An essential tool for this is an XML sitemap that lists all your pages. You can easily create an XML sitemap with All in One SEO or via the XML Sitemaps tool.
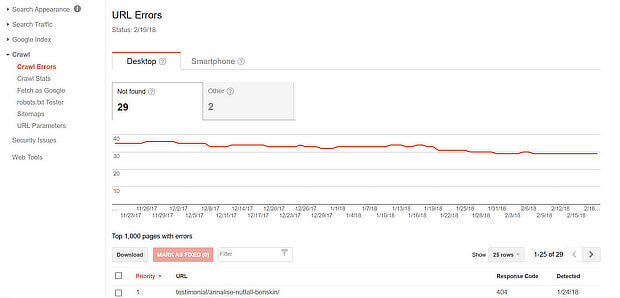
You’ll also need to check your site for crawl errors with Google Search Console. Log in, and go to Crawl » Crawl errors to see how your site is doing.
Learn more about doing an SEO audit for site crawlability here.
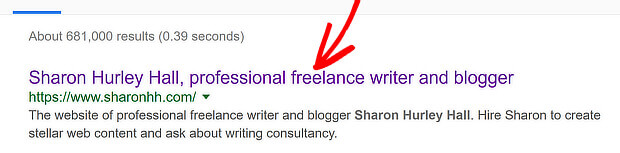
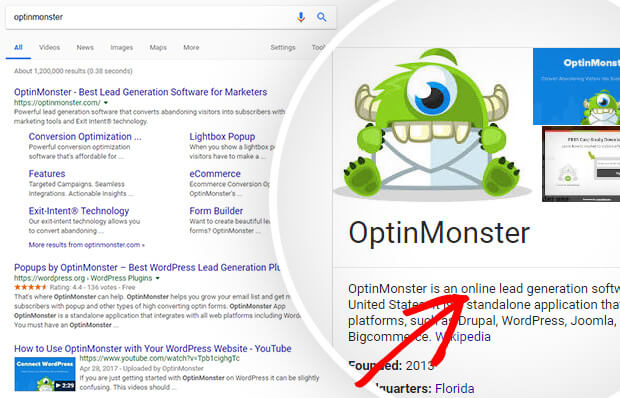
Step 2: Secure Your URL
A secure website URL, like the OptinMonster example shown earlier, is an essential SEO ranking factor.
Not only do you need to enable HTTPS, but you also need to check your site for other security issues, like:
- Having some site content that isn’t secure
- Linking to insecure content
- Ensuring your security certificate is valid.
Here’s a guide to checking the SEO aspects of site security.
Step 3: Use Canonical URLs
It’s also essential to get your site’s URLs right for good SEO. There are two aspects to this.
First, check that you’re telling Google which page is the most authoritative on a topic by using a canonical URL.
Second, make sure you’re using readable URLs that aren’t over-long, filled with weird characters or are too hard for visitors and search engines to understand.
Step 4: Optimize Page Titles and Descriptions
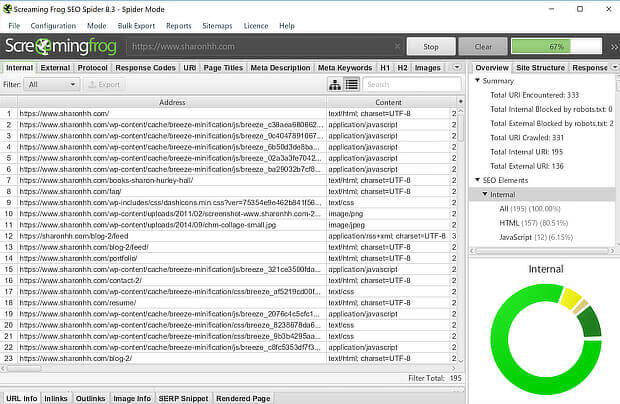
Page titles and descriptions affect what people see in search results, so it’s essential to check these out in any SEO audit. Screaming Frog SEO Spider is a great free tool for doing this.
To use Screaming Frog, type your main site URL into the search box, and you’ll soon be able to see all the page titles and meta descriptions it finds (up to 500 in the free version of the software).
Look out for missing or duplicated page titles and empty meta descriptions, which can result in reduced search engine ranking.
Step 5: Look After Content Hierarchy
Content hierarchy (letting Google know which content on a page is most or least important) is an essential aspect of SEO. One way to show this is with header tags like H1, H2, and H3. You can easily assess header tag use with Screaming Frog, as described in this guide.
Step 6: Optimize Images
As mentioned earlier, images are indexed, too, so checking they’re optimized for image search is an essential step in any SEO audit. Ideally, images will:
- Include a descriptive filename
- Have alt text which describes them, and is also good for accessible
- Be compressed, so they don’t slow down page load times
You’ll also want to check that links to images work as they should, and aren’t broken.
You can troubleshoot image issues via the SEO Audit tool in SEMrush:
Learn more about performing an image SEO audit here.
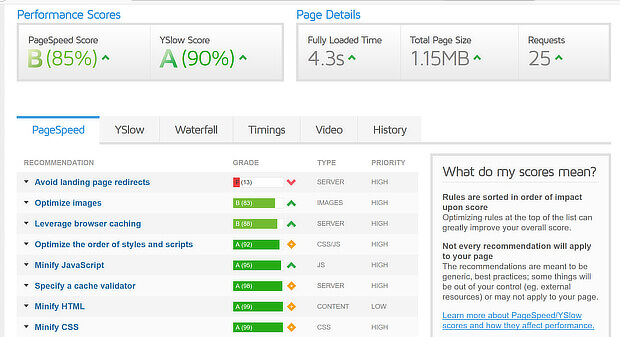
Step 7: Check Site Speed
Keeping images compressed minimizes site load times, but it’s not the only factor to look at. Sites can also be slow because of having too many page requests, too many scripts, and unoptimized code. A good SEO audit will help you find and fix these issues.
This is important because slow sites turn visitors off, and reduce your site’s potential to make leads and sales.
Plus, if people bounce away because the content hasn’t loaded, that affects dwell time. As we saw earlier, that’s an important SEO metric.
Learn how to measure site speed with tools like GTMetrix here.
Step 8: Use Structured Data to Classify Your Content
Structured data, also known as schema markup, is a way to classify your content to help Google show even more relevant results.
Using structured data can help Google work out whether a search for “spiders” relates to arachnids or search engines, for example.
Examples of structured data in action include recipe cards and answer boxes, which give searchers a complete—or almost complete—answer to their search query.
Here’s a guide to auditing and optimizing structured data on your site.
Learn even more ways to fine-tune your SEO audit in our guide.
6. How To Build Links For SEO
If you’ve read from the beginning, you know that links are a key SEO ranking factor. That makes link building an essential SEO practice.
Whatever you do, don’t buy links: Google won’t like it.
Instead, concentrate on two valuable link types:
- Earned links, which you get when external sources choose to link to your content
- Created links, which you get from taking part in external promotions like guest blogs and expert roundups and interviews
One of the most important aspects of links is the quality, because that builds authority, and helps your content rank higher.
High-quality content usually results in high-quality links from well-respected sites. That passes on link juice, which helps boost your search ranking.
Link juice, sometimes called link equity, is the value and authority that a web page link or site link passes to another web page as far as Google is concerned.
We talked about links earlier, but here’s a quick recap. When you’re talking SEO, the most important links are:
- Internal links to your own content
- Outbound links to other quality sites
- Inbound links or backlinks from other sites to yours
You also need to think about whether links are dofollow, and pass link juice, or nofollow, and don’t.
To attract great links you’ll need to:
- Get strategic about content creation, including optimizing content as described earlier
- Write great headlines and great copy that attract your audience
- Use attractive images that grab the eyeballs
- Use guest blogging, and take part in expert roundups and interviews to earn links
A good way to keep track of links is to use the site audit tool built into SEMrush. After you’ve set up a project to track site metrics, as described earlier, go to SEO Toolkit » On Page & Tech SEO » Site Audit.
As we saw earlier, that’ll give you a report on links to your site, and will even tell you which links are potentially toxic and are worth disavowing.
Here are some more tips on getting linking right.
- Make it a habit to interlink your content every time you write something new, and be sure to regularly go back to old content to add links to newer content.
- Make sure Google can crawl your site with an XML sitemap, as described earlier.
- Find and fix broken links, both internally, and those to external resources.
- Encourage people to review your products and services.
- Add your product to a service like G2Crowd – once those reviews are up, they appear in search engine results.
Want to find missing links, where people have referred to your brand but not linked to you? This is a time-honored SEO practice called broken link building.
You can use BuzzSumo for this. Just set up an alert for your brand and BuzzSumo will show you where there’s a missing link.
Then use a tool like OutreachPlus to manage outreach and ask for the link. This can help you enrich your inbound link profile.
You can also find linking opportunities by locating people publishing in your niche via BuzzSumo. To do this, search for your topic and see the sites that are publishing the most shared content.
For each site, use Moz’s Open Site Explorer to find the site’s domain authority. If it looks like a good linking prospect, then approach the site owner and explain briefly why you think your content might be a good fit.
Learn more about this in our guide to SEO link building.
Be warned: all link building is NOT created equal. There are some spammy link building practices that’ll hurt your SEO. We’ll look at these more in the section on black hat SEO.
Before we do, let’s check out a couple more important areas for SEO: social media and mobile. We’ll start with social.
7. Social Media And SEO
We said earlier that social media isn’t a direct SEO ranking factor, so you’re probably wondering why we’re even mentioning it.
It’s because it does have an indirect impact on search rankings. Smart marketers don’t ignore it—they take advantage of it to boost their rankings.
So, how does that work exactly?
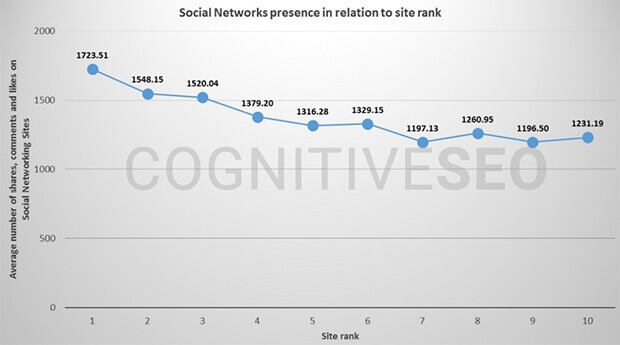
Research from Cognitive SEO and others shows a relationship between search rankings and social signals.
It’s pretty clear there’s something going on. Plus other search engines—yes, there ARE others—like Bing state clearly that social IS a ranking factor for them. Just something to think about.
So what’s the deal?
Actually, it’s simpler than it looks. Remember that links, content, and user experience are all major SEO ranking factors.
Well, social media amplifies other ranking factors by making your content more visible. When more people see it, more people link to it. The more people link to it, the more it’s seen as authoritative, and the more likely it is to appear in a good position in SERPs.
There’s proof.
According to Matthew Woodward, content that got thousands of Facebook shares gained a couple of top ten search positions, plus an answer box listing.
So, how do you optimize the content on social networks for better SEO? Here are some tips:
- Give your profile a consistent image, a relevant bio and, where possible, a link (perhaps to your lead magnet)
- Post regular social media updates so your accounts are active
- Improve your updates with catchy titles and attractive images
- Ask people to share for even more amplification
- Use hashtags if appropriate
- Make your content easily shareable
Check out this guide for more detail on social media and SEO.
Next, let’s look at mobile SEO.
8. Mobile SEO Guide
The rise of mobile devices has shaken everything up, and that includes SEO.
With recent Google changes, failure to look after mobile SEO could result in search invisibility, and mobile’s bringing other changes you’ll need to be ready for.
Here’s the deal.
What Is Mobile SEO?
Mobile SEO is mobile search engine optimization or optimizing content for a better search ranking.
Google has 95% of the mobile search market, so optimizing for mobile means optimizing for Google.
Some key information to know is:
- There are more mobile searches than desktop searches
- Google now has a mobile-first index
- Mobile searches where people are looking to buy have increased
- Mobile search gets you ready for voice search, which is growing
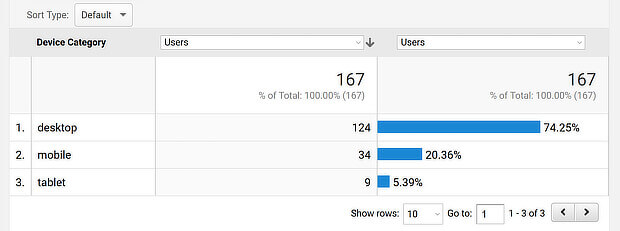
One thing it’s worth doing is checking how much mobile traffic you have. That way you’ll know if you should already be looking after mobile SEO, or you have a couple of weeks to do it.
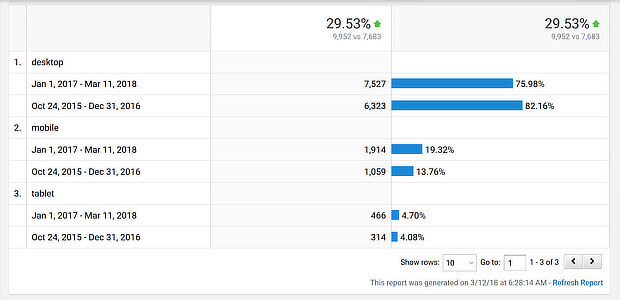
Go to Audience » Mobile in Google Analytics. You’ll see stats for desktop, mobile and tablet traffic.
Then click on the onscreen date selector and compare current data with data from a year ago.
We’re willing to bet that those numbers have changed, and there’s now more mobile traffic and less desktop.
Check Your Site For Mobile-Friendliness
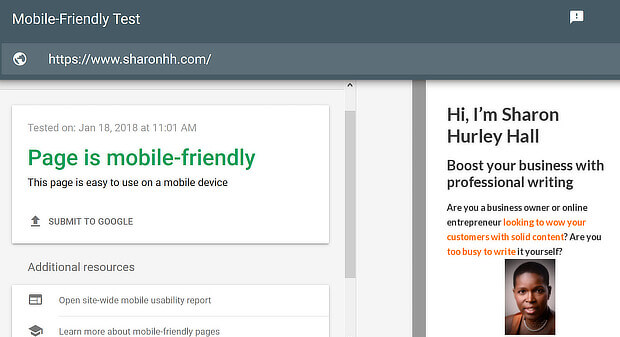
If you’re getting started with mobile SEO, it’s a good idea to check if your site is mobile-friendly. One of the easiest ways to do that is with Google’s own tool.
Type in your site’s URL, run the test, and you’ll soon see if your site’s mobile-friendly and what the recommended fixes are.
You can also check your site for errors in the Crawl Errors section of Google Search Console, as described earlier, looking at the mobile tab, of course.
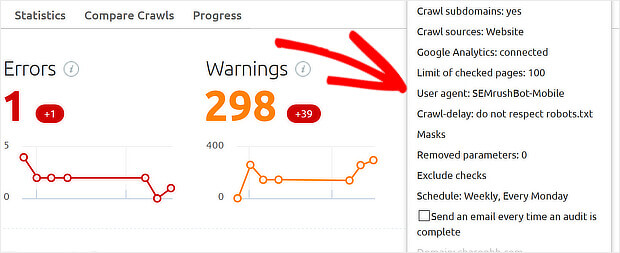
And you can use SEMrush’s site audit tool if you change the user-agent from desktop to mobile as shown below.
Mobile SEO Issues
For mobile SEO, some of the same issues apply as on the desktop. For example, since you want to increase dwell time, it’s important to reduce bounce rate.
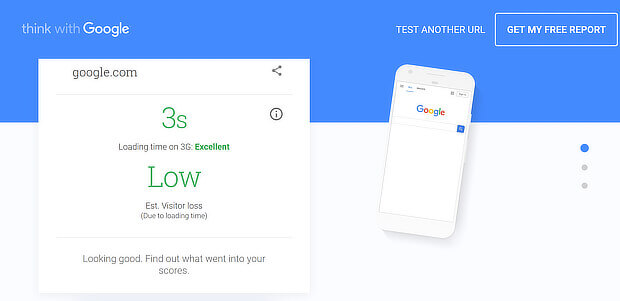
With mobile devices, this often means having a fast loading site because you’ll lose more than half your visitors if your site takes more than three seconds to load. Use Google’s mobile speed test to check this.
One mobile-specific step to take includes setting up AMP (accelerated mobile pages) on your site for a fast experience for visitors.
To create a good mobile user experience, you also need a responsive design which resizes according to screen size. WordPress sites can handle this easily by using the right theme. Otherwise, check out Google’s own guidelines.
You can also optimize your content so it meets the guidelines for “eyes-free” search. That means:
- Having your content answer questions correctly
- Formulating answers correctly
- Keeping them to 29 words or so
Mobile SEO And Your Marketing
Another thing that affects Google’s perception of your site is how you market. In particular, Google dislikes zero-second popups which make for poor user experience.
Since OptinMonster’s all about user experience, you won’t be surprised that we hate them too. That’s why we’ve made sure we have device-specific display rules, behavioral triggers like Exit-Intent®, MonsterLinks™ 2-step optins, and mobile-friendly themes.
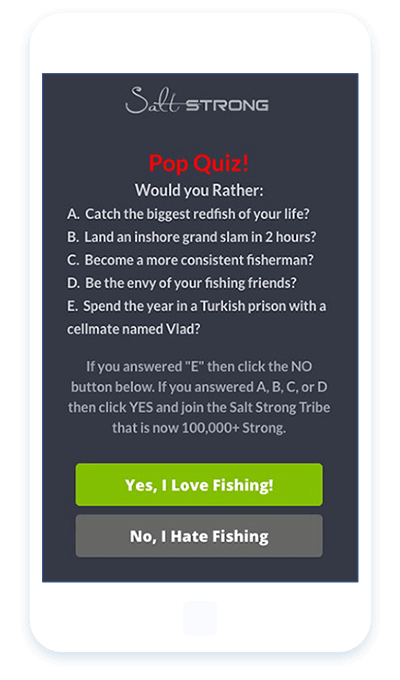
Not only will you avoid annoying visitors; you could also increase conversions by 185% like Salt Strong did, while still increasing organic traffic.
Learn more about mobile SEO here.
9. The Best Keyword Research Tools
If you’re improving SEO, you’re going to need a few tools. We’ve mentioned a couple of them already, but here’s a full list of the keyword research tools we like. Many of these go way beyond keyword data to help you analyze different aspects of your marketing.
- Ahrefs is an all in one toolkit to help you improve search traffic.
- Answer the Public shows you the questions searchers ask to help you with content targeting.
- Bing includes a keyword research tool in Bing Webmaster Tools. The tool provides volume and keyword suggestions.
- Google Adwords Keyword Planner provides monthly global and local keyword search volumes.
- Google Trends is a useful tool for deciding which of several similar search terms is more popular
- Keyword Eye brings together keyword data from Google, YouTube and Amazon, and helps you find keywords, questions, and competitors’ keyword and advertising data, as well as trending content.
- Keyword Spy is a downloadable keyword tool which helps you to identify competitors’ keywords and find related terms you can use in your own content and marketing.
- Keyword Tool is a free online tool that generates around 750 Google keyword suggestions. It also offers keyword suggestions for Bing, YouTube, Amazon, eBay and Apple’s app store.
- Long Tail Pro includes a number of useful keyword research features. As well as simply finding keywords, you can assess ranking difficulty, competitiveness and can filter results in various ways, such as by local search.
- LSIGraph provides a long list of Google autocomplete suggestions.
- Moz Keyword Explorer allows you ten free searches a month. If you need more, you’ll need to upgrade to Moz Pro. You can search for keywords to find related terms and search volume. You can also filter results according to similarity, volume, and range of sources.
- SEMrush is a comprehensive marketing toolkit that includes a lot of SEO tools. You can try out a free keyword search on this page.
- The SEO Book Keyword Suggestion Tool aggregates search data and provides volumes, related terms, and more.
- The free SERPS keyword research database lists related terms and provides search volume, cost per click and value for each keyword phrase.
- Soovle provides autocomplete suggestions from multiple sources on a single page. In addition to Google, YouTube, Amazon and Bing, it includes data from Wikipedia, Answers.com, and Yahoo.
- SpyFu is a paid tool that uses 11 years of historical data to help you find your competitors’ most profitable keywords and the keywords they’ve used for SEO and ads.
- Ubersuggest provides lists of keywords, though you’ll have to install the Keyword Everywhere extension to get search volume and cost per click data.
- Wordstream Keyword Tool: This tool uses browser searches, information from internet service providers and search data to include a wide keyword database. You can get 10 free searches, then one daily search for free.
Bonus content: Discover the Best SEO Plugin for WordPress: Expert Picks!
10. How To Use SEO For Lead Generation
As we’ve seen, one of the major advantages of SEO is getting more traffic because of better search ranking. That makes SEO an ideal lead generation tool, because when searchers follow links back to your site, you have the chance to convert them to leads, and later make sales.
Your website is one of your best lead generation tools, and SEO funnels traffic to that tool. The better you get at SEO, the more traffic—and more leads—you’re likely to attract.
Why use SEO for lead generation? Well, cold calling doesn’t work anymore and people tend to block or ignore ads.
That means that relying solely on paid traffic isn’t a good strategy. Instead of marketing at people, you need to make it easy for them to find you when they want you, and that’s where SEO comes in.
Unlike the old days, customers find information long before they’re ready to talk to you. So you have to put that information out there, and help them to find it easily.
That means working out what your content marketing mission is and using the right content types and distribution channels to reach your audience. But before you do any of that, you need to work out your SEO strategy. Here’s how you do that.
Know Your Audience
First, figure out who you’ll be optimizing content for by creating buyer personas. These include your target customers’ age, gender, income, and education level; their key sources of information; and their main challenges and pain points.
Know Your Leads
Next, work out what you consider a lead, as this varies for each business and situation. For one business, a lead might be someone who opts in to an email marketing campaign. Another lead may download a lead magnet. For yet another lead, free trial signup might be the sign of a qualified lead.
Some of the SEO practices we’ve outlined in this guide also help with lead generation. Let’s just recap those quickly:
- Identify keywords you can use to create content
- Audit existing content for potential optimization opportunities
- Create or optimize content, paying attention to titles, meta descriptions, the content itself, answer box opportunities, and links
These steps will help you attract traffic to your site, but to turn them into leads, you’ll need to do a bit more.
That’s where OptinMonster can help. Our advanced marketing software gives you multiple ways to convert your visitors into leads and paying customers.
Here are three proven methods to do just that.
1. Create a Lead Magnet
First, create a free download, such as an ebook or PDF checklist or cheat sheet, that you can offer in exchange for your visitors’ email addresses. This is called a lead magnet.
Then you can use OptinMonster to capture subscribers and deliver your lead magnet.
Since OptinMonster integrates with the most popular email marketing services, collecting those emails will be easy. Just follow our instructions for creating your first campaign or check out the video below:
Once that’s done, go to the Success view in the OptinMonster campaign builder.
The default option is to have the download link sent via email, but you can add a Download Now button with some easy customizations.
Let’s add a new Column to our design to house the button. We’re going to add the Column with three equal sections, but you can choose whichever works for the look you want.
Follow the same drag and drop method to add a Button Element to the new Column you just created.
Click on your new Button to customize it.
Add your download URL. Turn on conversion tracking if you’d like.
Publish your campaign, and you’ll soon start getting some leads.
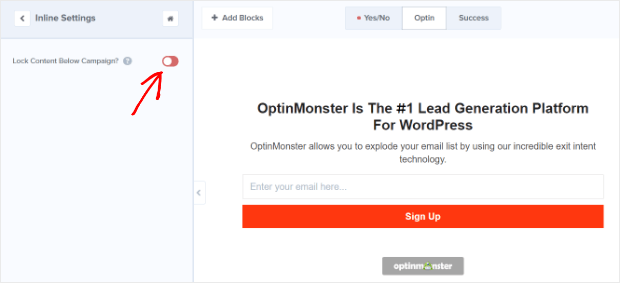
2. Use Gated Content
Gated content is another great way to encourage people to sign up. Photowebo got a whopping 3806% increase in conversions with this technique.
With gated content, your visitors will have to enter their email addresses to get access to your most valuable content. This works incredibly well when you use it on your most popular blog posts that are long and in-depth.
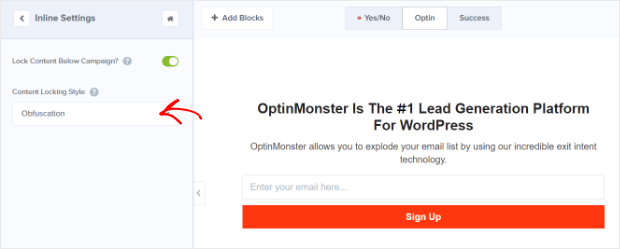
To lock content in OptinMonster, create your campaign. In the campaign builder, go to Inline Settings and turn on Lock Content Below Campaign by clicking the toggle.
Choose a method. We’ll use Obfuscation, which completely hides the gated content.
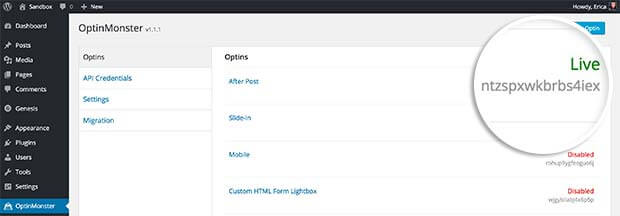
Grab the embed code and paste it into your post or, if you’re using WordPress, go to your dashboard. Here, you’ll get optin slug from under the Live link.
Add it to this text in place of “SLUG” to create a shortcode you can embed in your content.
3. Use Exit-Intent® Technology
OptinMonster’s exit-intent® technology is a great lead generation tool which grabs visitors’ attention with an offer or content just before they leave your site.
Exit-intent offers are incredibly effective. Ryan Robinson used exit-intent to increase subscriber numbers by 500%.
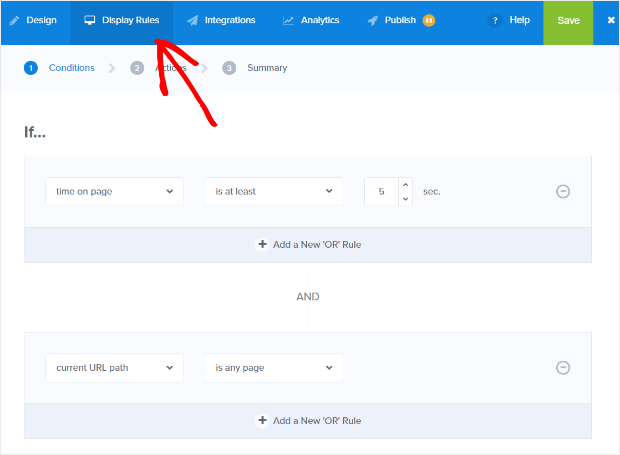
And it’s pretty simple to enable it in the OptinMonster campaign builder. Once you’ve created your campaign, Go to Display Rules.
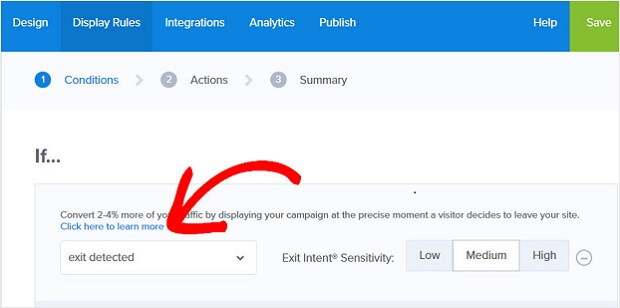
Change the condition to If exit detected:
Learn more about SEO for lead generation, and check out these expert strategic SEO tips.
FAQs About SEO
We’re almost done with our in-depth SEO guide, but before we go, let’s answer a few common SEO questions.
What is White Hat vs Black Hat SEO?
You may have heard the terms white hat SEO and black hat SEO. Taking its cue from old-time Westerns where the good guys wore white hats and the bad guys wore black ones, the difference between white hat vs black hat SEO is the difference between accepted SEO practices and ones that are seen as less ethical.
White hat SEO includes all the SEO practices we’ve talked about so far which take a long term approach to site optimization and focus on the user experience and what people need.
In contrast, black hat SEO is about trying to take shortcuts and game search engines. This rarely works. And, black hat blog posts and content can get you penalized.
Black hat SEO practices to avoid include:
- Keyword stuffing
- Thin content
- Automated comment spam
- Content scraping
- Cloaking, hidden text, and doorway pages
- Sneaky redirects and malicious site behavior
- Link schemes
Learn more about white hat vs black hat SEO in our guide.
Are Google search results personalized?
Sometimes. Google encourages you to log in to your Google account and to link it to your Chrome browser. And it also collects your search history. That can result in personalized search results. If you want to avoid this, you can search in an incognito or private window so you get the true picture on SEO.
Is search engine optimization dead?
As Mark Twain once said, sorta, the death of SEO has been greatly exaggerated. As you’ve seen, there are some SEO practices that used to work that don’t work anymore. But there’s also plenty of information right here in this guide about the SEO practices that work. And we know they work because we use them too.
How do you get to the top of Google search results?
Here’s the truth—only one site can be number one for a particular keyword, and there’s a lot of competition out there. But optimizing your site can make a difference to which site that is, as rankings fluctuate all the time. Plus, as long as you’re in the top 3, or at least on the first page, you’ve got a chance for people to find and click, which is what you want. If you deliver what they need after the click, that increases your chances of being relevant for future searches for that term.
Why is SEO so important?
If you don’t look after SEO, you can get lost among the trillions of links out there. SEO gives you a shot at ranking for the terms which your customers use, so you can do better business.
That’s it!
Now you know just about everything we know about SEO, and we’ll keep this guide updated so it’s always got the latest best practices and guidelines to make SEO easy. Want more? Check out these SEO statistics!
Next, check out our guides to email marketing and growth hacking to help you promote your business for even more growth. And follow us on Facebook and Twitter for more tips and guides.
























Add a Comment