Did you know that more than 90% of online shoppers invest time to compare pricing?
Product pricing touches nearly every aspect of your eCommerce business, from cash flow to profit margins, but with so many ways to price a product, it’s confusing to know which strategy to use.
Should you use odd pricing, the rule of 100, or bundle pricing strategy? What even are those things? Do you need to change the pricing in your entire catalog, or can you just change a few products here and there? And what are your competitors doing?
In this post, we’ll walk you through how to price your product in six easy steps.
Step 1. Work With Accurate Competitive Pricing Data
According to Lemonstand, 60% of all online shoppers name price as one of the most important factors affecting online purchasing decisions. Shoppers use comparison websites, so it makes sense for you to know how your competitors are setting their product prices too, right?
But, how can you find accurate competitive pricing data?
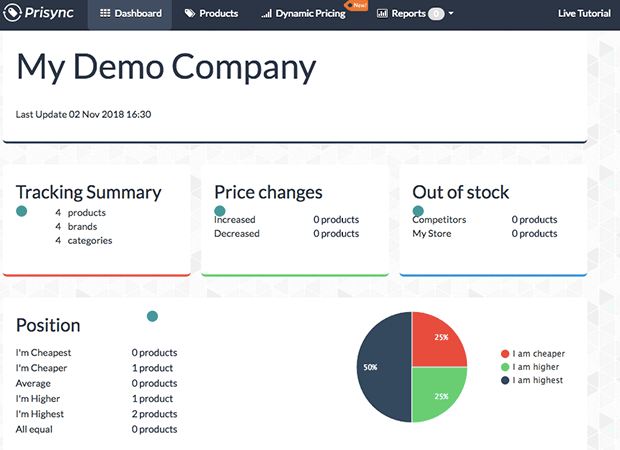
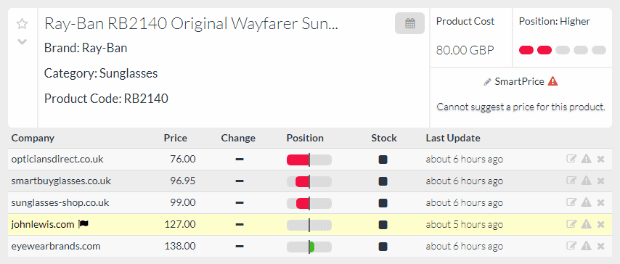
One way is to use a platform that has the ability to collect, analyze, and compare pricing data. This gives you the information you need to make decisions about your pricing structures and provides an opportunity for growth.
For example, by knowing your competitor’s product pricing, you can promote the product that your competitor has on full price. Using an automated competitor price tracking software such as Prisync can save time and boost your sales.
With this type of software, you can look at individual products to see how your pricing measures up to your competitors:
Check out our list of the top 25 competitor research tools to give you the advantage.
Step 2. Don’t Worry About Uniform Pricing Changes Across Your Catalog
Some businesses think that if they raise or lower prices for one product or a handful of products, they have to change prices across their entire catalog. Let us assure you that’s not the case.
Instead, you can customize your pricing on a product-by-product basis. Raise or lower your pricing based on market demand or competitor pricing, but remember: it’s important not to lower your prices too low, or you may risk cutting into your profits. On the other hand, if you raise your product prices too high, you run the risk of losing sales to your lower-priced competition.
Step 3. Use the Right Pricing Model
While a number of factors can affect your business’s revenue potential, one of the most important is the pricing strategy. Here are four common pricing strategies to consider:
Premium Pricing
In this pricing model, you set your price higher than your competitor’s. This strategy is most effective for small businesses that sell unique products.
It’s also best to use this pricing strategy when you first introduce a product when there is limited competition.
Economy Pricing
Targeted at the most price-conscious consumers, this strategy minimizes costs associated with production and keep product prices low. Economy pricing is most effective for big businesses, as they have the volume and resources to sustain the low prices of their products.
Psychology Pricing
Psychology pricing encourages customers to make a purchase decision based on an emotional trigger rather than a logical one.
The rule of 100 is an example of the psychology pricing model where customers tend to purchase more products set at $11.99 compared to products set at $12.00, even though the cost difference is only $0.01. The psychology behind this is that customers tend to focus on the first number on the price tag, rather than the last.
Bundle Pricing
With the bundle pricing model, you sell multiple products at a lower rate than if a customer were to purchase the product individually. This strategy increases the value perception in the eyes of the customer as they’re paying less per product, but it’s also working to increase your average order value.
As a bonus, this is also an excellent way to move unsold products from your inventory.
Step 4. Maintain Communication Between Teams
Pricing changes impact a lot more than finances; they impact relationships too. That’s why it’s so important to keep lines of communication open between teams, vendors, suppliers, and particularly those with customer-facing roles.
Customers tend to view a product price increase as fair when the company communicates the change directly, so be as transparent as possible in your customer communications. This is especially important if you are increasing prices.
Step 5. Maintain Positive Price to Value
Customers want to know that they’re buying a product that has a positive value. They want to feel like they’re getting more than they paid for. It’s really got more to do with the perceived value (the customer’s opinion of the value a product), rather than the actual market value.
You can make sure that customers know the value of your product by writing a compelling value proposition for each of your products.
Your product’s value proposition describes your target user, the problem the product solves, and why your product is better than anything else out there.
Step 6. Pay Attention to Promotional Timing
Did you know that 91% of consumers check their emails at least once a day? Or that 86% of consumers have made a purchase as a result of an email they received?
Timing can have a huge effect on open rates, so it’s important to find the best time to send your emails.
In general, the best days to send out emails are weekdays (Monday through Thursday), while weekends tend to drop like a rock for email engagement. As for time of day, late mornings during the week are peak open rate times.
There you have it! You’ve just learned how to price a product in six easy steps. Now, check out our post on how to create a countdown popup that can you help put your pricing to work. Or, you can always try one of our other awesome tutorials!
Not using OptinMonster yet? No problem. You can join RIGHT NOW.












Add a Comment