Are you trying to increase your traffic and search rankings, but aren’t sure what to do? An SEO audit is the perfect place to start.
Search engine optimization can be tricky these days, especially if you don’t know what’s working and what isn’t. Fortunately, an SEO audit can show you how you’re doing and what needs to be improved.
In this article, we’ll go over everything you need to know about SEO audits so you can do one yourself any time you need to.
Here’s a table of contents to help you find your way around:
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a detailed check of how well your website is ranking in search. In an audit, you’re comparing your site’s performance against your competitors as well as your own previous performance.
Performing an SEO audit is the only real way to see whether your SEO strategies are working. Think of it like a test at school. You may attend all the classes and do all the assignments, but the real test of your knowledge is when you take the final exam.
What Should an Seo Audit Include?
An SEO audit should include these 4 categories of SEO ranking factors:
- Basics: Can search engines even find your site? If yes, proceed.
- Technical SEO: Does your website meet the requirements of modern search engines?
- On-Page SEO: Is your content and HTML source code optimized to help readers meet their goals?
- Off-Page SEO: Do other websites consider your site to be a reputable authority on your topic?
We’ll go into more detail about each of these areas in the audit checklist below.
Manual vs Automated SEO Audit
You may be wondering whether there’s a way to automate your SEO audit.
There are certainly some automated SEO tools that can give you a good start. We’ll recommend some of our favorites in the checklist.
But relying on automated SEO tools alone isn’t enough. No software can understand your business and audience the way that you do. So you still need to know what all the search engine ranking factors are and how to influence them.
Why Do I Need an Seo Audit?
You need to do SEO audits regularly in order to grow your organic search traffic. After all, you can’t improve what you don’t track.
Without enough traffic, the rest of your digital marketing and sales funnel is useless. You may have a high conversion rate on your sales page, but if only 3 people ever see that page, you won’t make enough sales to stay in business. Organic traffic is far cheaper to acquire than advertising, so you must make an effort to rank in searches.
Plus, your competition is always changing. The main goal of an SEO audit isn’t to imitate your competitors or let them tell you what to do, but it’s still important to know what they’re doing.
Your business may also be changing. As you add new products and services or reposition yourself in the market, you may need to rank for different search terms or long-tail keywords. So regularly checking on your search performance will help you avoid losing traffic.
When Is an Seo Audit Needed?
You should audit your SEO on a regular basis. How often depends on how much you’re publishing. We recommend doing SEO audits at least 2-4 times per year.
Think of it like going to the doctor for regular checkups. Checking in regularly makes it easier to catch issues that need attention and make small adjustments. Waiting until you’re very sick to see a doctor might mean you need major surgery or a hospital stay to feel better.
Best SEO Audit Tools
Before we dive into the checklist, we wanted to share some of our favorite SEO audit tools you can use to check your SEO.
Like we said before, no tool can fully replace a detailed understanding of how SEO works for your business. But there are some great plugins and websites out there that can speed up your SEO audit.
Here are our top picks:
1. All in One SEO
All in One SEO is the best WordPress SEO plugin for optimizing your technical, on-page, and off-page SEO.
The plugin is easy to use for bloggers, business owners, designers, and anyone using WordPress. There’s a full toolkit of on-page SEO optimization tools, schema markup, search appearance settings, link assistant, and more.
There’s even a built-in site audit checklist that can help you stay up to date on your site health in between formal SEO audits.
2. Semrush
Semrush is a search engine marketing software with powerful functionality. The site audit tool automatically checks over 130 technical and on-page SEO factors. You can customize your reports for crawlability, site performance, international SEO, and more.
Semrush also lets you track your search engine results page (SERP) positions and discover millions of relevant keywords.
Alternatives: Ahrefs, Moz
3. Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is a technical SEO powerhouse. Our favorite feature for SEO audits is the SEO Spider.
SEO Spider can find broken links, redirect chains and loops, duplicate content, unoptimized page titles and metadata, and other technical SEO issues on your site.
4. Google Analytics
Google Analytics provides an overall view of your website traffic, including search traffic. You can see engagement metrics for each page and how well your landing pages are converting.
If you notice a high bounce rate on certain web pages, you can refresh the content and optimize the page in other ways. Or you may notice a lot of traffic coming from certain referral sources, which can show that your link-building strategy is working.
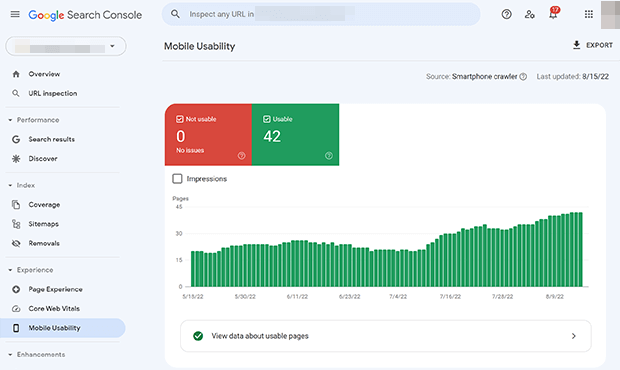
5. Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google that lets you monitor your presence in Google search results.
You can check your site’s crawlability and detect indexing or spam issues, You can also check out your site’s backlinks and keyword ranking positions.
How Do I Run an Seo Audit?
Now let’s look at how to run a complete SEO audit. We’ll go through each of the 4 major categories of ranking factors. It’s a long list, so here’s a table of contents to help you find your way around:
Let’s get started!
Part 1: Check the Basics
If search engines can’t crawl your site, none of the steps after this matter at all. So the first thing to do is make sure search engines can find your site in the first place.
1. Crawlable Status
Crawling means that the search engine visits pages on your website. Then it adds optimized pages to the search engine index, making them available for users to find.
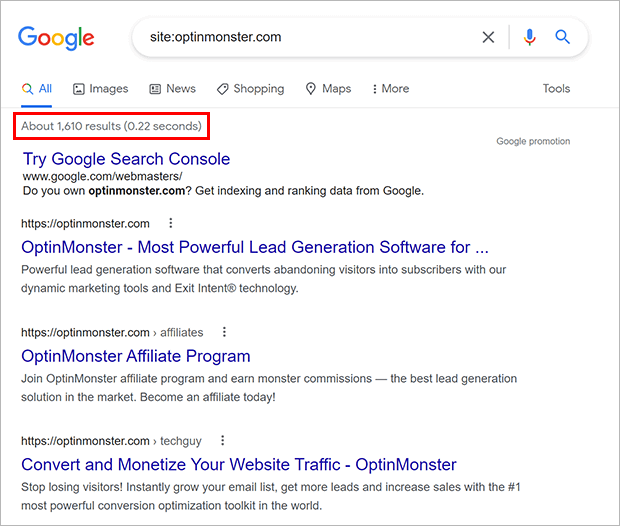
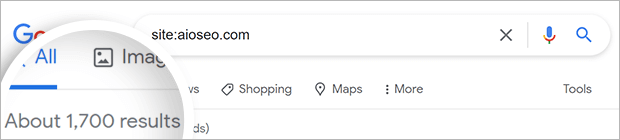
The easiest way to see if your site is crawlable is to search for your domain on Google with the prefix site: or info: in front of it.
If your site is crawlable, you’ll see a list of pages. If your site isn’t crawlable, you’ll see a message that there are no search results.
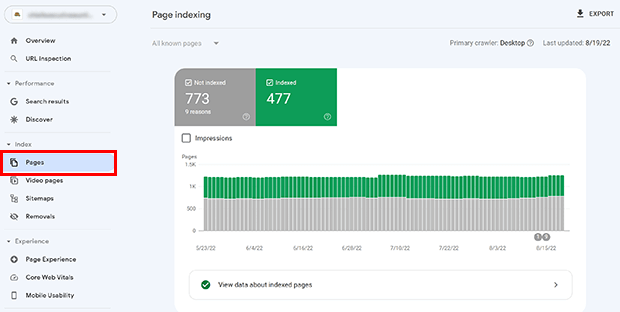
Another way is to check the Page Index report in Google Search Console.
If you need help making your website crawlable, check out these quick and easy ways to index your website on Google.
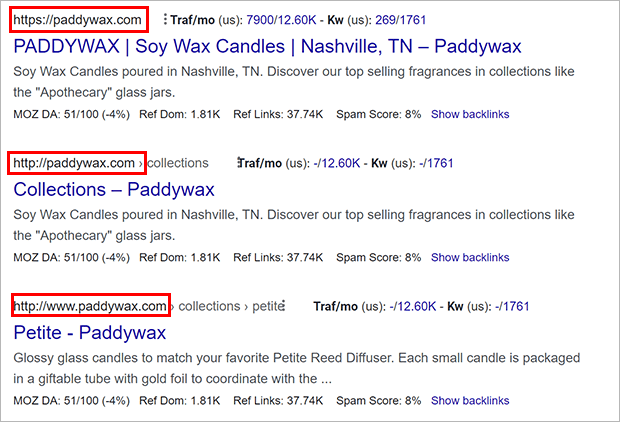
2. Duplicate Versions
The next thing to check is whether Google is indexing one or more versions of your site.
Your website could sit on:
-
-
- http://www.domain.com
- http://domain.com
- https://www.domain.com
- https://domain.com
-
While the average user may not notice a difference, a search engine sees these all as different versions of the site.
When you check to see if your site is crawlable in step 1, look for a mix of site versions.
If this is a problem, you need to specify canonical URLs.
3. Indexed URLs
This check can be done at the same time as steps 1 and 2, but it’s worth explaining further here.
When you run a site:search on Google, notice the number of indexed URLs.
If this is about what you would expect, you can move on.
If it’s higher or lower than you expected, you may have an issue with duplicate content, or your site may not be crawled or indexed correctly.
4. Manual Actions
If you violate Google’s webmaster quality guidelines, your site may receive a manual action from Google, formerly known as a manual penalty.
Manual actions can cause your Google rankings to drop until the action is revoked.
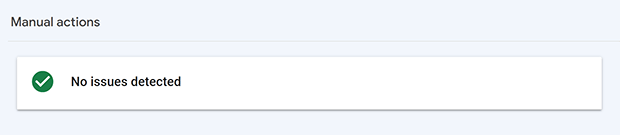
To see if you’ve received a manual action, go to Google Search Console. Look for the Security and Manual Actions section in the left menu. Click on Manual Actions.
Ideally, you should see a message that no issues were detected.
If there is a problem, look through Google’s guide on resolving and revoking manual actions.
Part 2: Technical SEO Audit
Now that we’ve checked the basics, let’s make sure your website meets the technical standards for modern websites.
5. Site Speed
Site speed is a critical part of user experience and page ranking. The slower a page loads, the more likely the user will bounce. A high bounce rate signals to search engine algorithms that your site doesn’t fulfill what users are looking for, so your rank will go down.
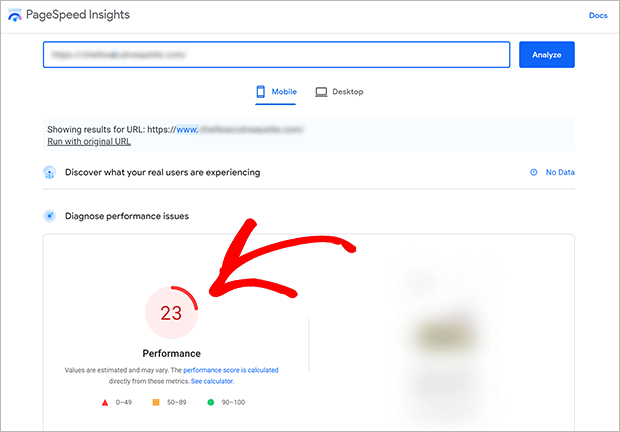
Google PageSpeed Insights is a quick and easy site speed testing tool. It will also give you recommendations on specific actions to improve your page speed for mobile and desktop.
6. HTTPS
Make sure your site is using the encrypted HTTPS protocol. This provides an extra layer of security for visitors, which will make them less likely to bounce from your site.
You can check your HTTPS status with Semrush’s Site Audit tool, or try AIOSEO’s SEO Analyzer if you’re using WordPress.
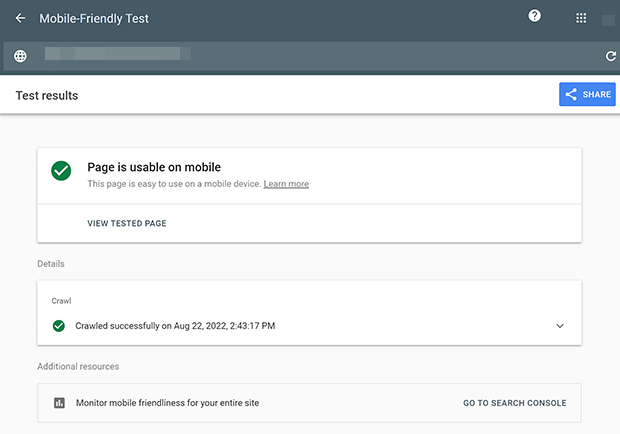
7. Mobile-Friendliness
Most people browse the web from mobile devices. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, many visitors will leave. It also looks unprofessional for your site to not be optimized for mobile.
Mobile-optimization is an important ranking factor. Fortunately, you can test your website with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
You can also look in the Mobile Usability section in Google Search Console.
8. Crawl Errors
When a search engine “crawls” your website, it follows the links from one page to another. This helps search engines understand the purpose and structure of your website. The easier it is to crawl your site, the better your chances of ranking higher.
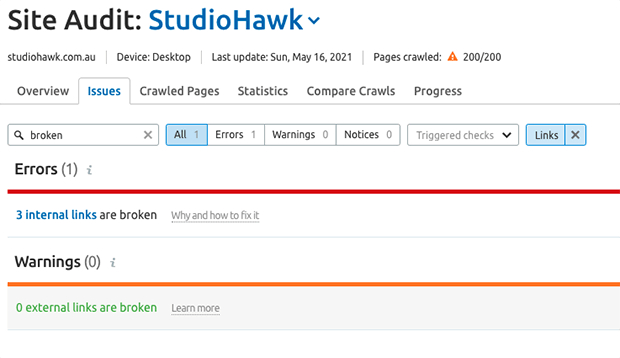
You can use Screaming Frog or Semrush’s Site Audit to look for crawl errors.
Common crawl errors include broken links and redirect chains.
A broken link is when a linked page doesn’t exist or can’t be found. This can happen if you change the URL of a page or mistype the link. Fortunately, you can easily correct this by changing the link URLs.
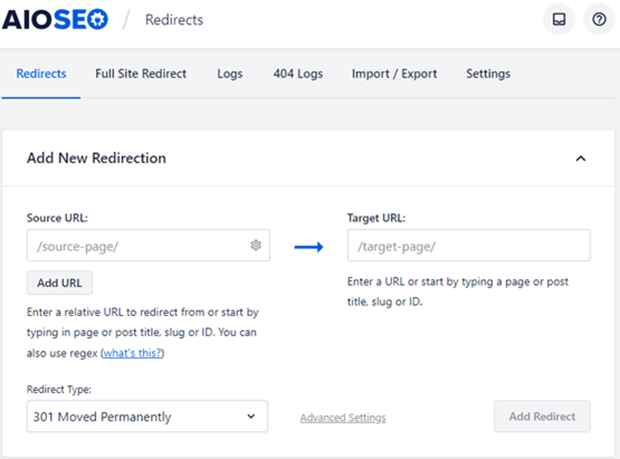
Redirect chains are when one redirect leads to another redirect and possibly more redirects after that. Fixing these can be a little more involved, but just make sure any redirects go directly to the most updated and relevant content.
All in One SEO has an easy-to-use Redirection Manager to help you out.
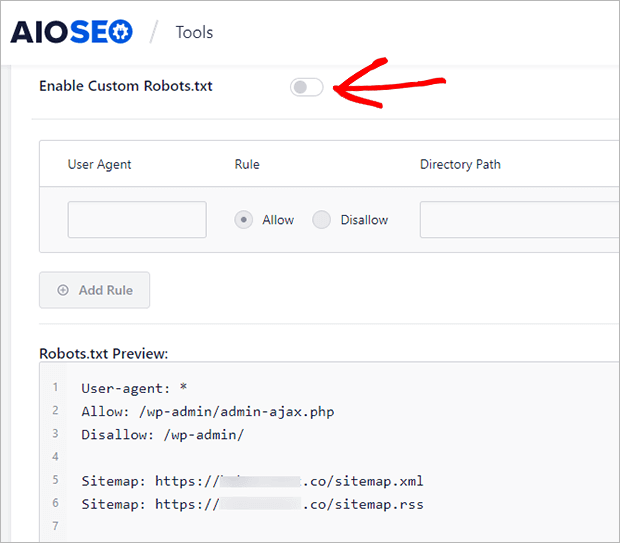
9. Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and display in search results.
Some pages aren’t worth crawling, such as:
-
-
- Admin pages
- Cart and checkout pages
- Login pages
- PDFs and other media files
-
So you want to periodically check that your robots.txt file is up to date.
You can create a robots.txt file manually and upload it to your site. If you have a WordPress site, you can use All in One SEO to easily edit your robots.txt file directly in WordPress.
Please note that in order to completely remove a site from the search index, you’ll need to use a noindex tag.
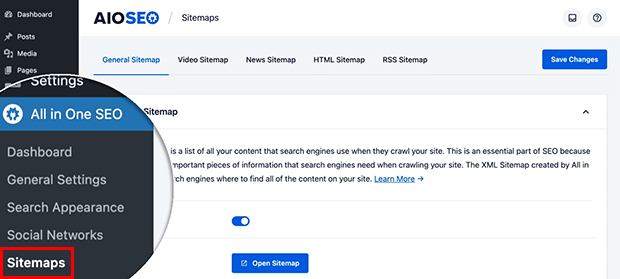
10. Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a blueprint of your site structure. It helps search engines find, crawl, and index your content more easily and often. Your sitemap also lets search engines know when you’ve updated content.
Coding a sitemap manually is possible but tedious. Instead, you can build a sitemap with Screaming Frog or All in One SEO.
Look over your sitemap and make sure it’s updated and accurate.
Part 3: On-Page SEO Audit
Now let’s look at on-page SEO. On-page SEO factors signal to search engines that your content is high-quality and useful. You want to use this checklist for every page and post, but for your audit, you can just check your homepage and most important pages.
11. Page Title and Meta Description
The page title and meta description have just one job: increase your click-through rate. So your title tags and meta tags need to be intriguing while also clearly telling users what the page is about.
If you’re using a target keyword for the page, make sure it’s in the title and meta description. Ideally, place the keyword toward the beginning. You also want to pay attention to how long your page title and meta description are.
12. SEO-Friendly URLs
Even the URL of your page can impact your SEO. Keep your URLs short and descriptive so that users can easily tell what’s on the page.
Shorter URLs also won’t get cut off in search results, and can get crawled faster.
12. Formatting
Formatting isn’t just to make your site look pretty. It’s an important part of readability.
Use headers and subheaders to organize your content. This makes it easier for readers to skim a page to decide whether they want to read it more carefully. Just make sure to not use any H1 tags in the body of your page. That title tag should be reserved for your page title.
Images can enhance the reading experience by breaking up large walls of text or explaining concepts visually. Adding alt text can help visitors who use screen readers, and that text also gets picked up by search engines as well.
14. Internal and External Links
Internal links to other pages on your website can help search engine crawlers understand the structure and purpose of your website.
On the other hand, external links show that you’re referencing external resources and not just your own perspective. This signals to search engines that your content is more reliable.
Make sure you’ve got at least one internal and one external link on each page.
13. Content Quality
You can’t just stuff keywords into a piece of content and hope to rank. You must deliver what you promise, or users will punish your site with high bounce rates and lower rankings.
A good rule of thumb is to make your content at least 300 words. But again, don’t just add words for the sake of adding words. Only make the page or post as long as you need to cover the topic in-depth.
Check out our full on-page SEO checklist to fully optimize your on-page content.
Part 4: Off-Page SEO Audit
After going through all the SEO ranking factors on your own site, let’s look at off-page SEO before we wrap up this SEO audit.
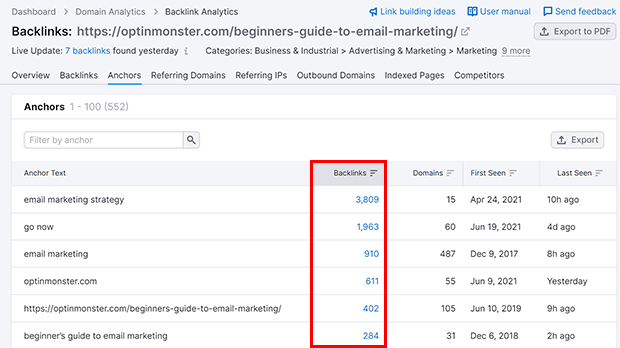
14. Backlinks
Backlinks are links to your site from other websites. The more backlinks you have, the more trustworthy and reliable your site appears to search engines.
To check your backlinks, you can use Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool or Google Analytics. Note that Google Analytics calls them referrals instead of backlinks.
You want to look for toxic backlinks. If you find any, you can contact the site owner to remove them, or disavow the most toxic backlinks.
You also want to check that the anchor text for your backlinks aren’t all one type of anchor text. For example, here at OptinMonster, we’d like to see a mix of generic, branded, long-tail and other types of anchor text.
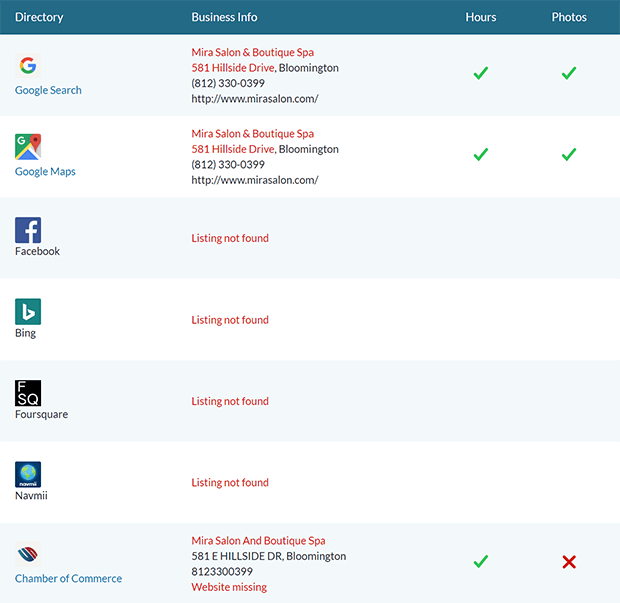
15. Local SEO
Finally, if you’re a brick and mortar business or serve customers in specific areas, you’ll want to check your local SEO.
A good way to do this is with Moz Local. You can look up your business by name and address and check your business listing visibility on different directories and social media platforms.
From the search results, you can check each individual listing to make sure the hours, photos, reviews, and other information are accurate.
There you have it! This complete SEO audit checklist is lengthy, but regular checkups will ensure that you aren’t wasting your SEO efforts.
Now that you know where you’re at, check out our expert SEO tips to boost your search traffic even more.
If you’re ready to supercharge your WordPress SEO, get started with All in One SEO today!
If you like this article, also check out: How to Perform an SEO Audit in 17 Easy Steps











Add a Comment